Dart Function
Dart Function
Dart function is a set of codes that together perform a specific task. It is used to break the large code into smaller modules and reuse it when needed. Functions make the program more readable and easy to debug. It improves the modular approach and enhances the code reusability.
Suppose, we write a simple calculator program where we need to perform operations number of times when the user enters the values. We can create different functions for each calculator operator. By using the functions, we don't need to write code for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and divide again and again. We can use the functions multiple times by calling.
The function provides the flexibility to run a code several times with different values. A function can be called anytime as its parameter and returns some value to where it called.
Advantages of Functions
The few benefits of the Dart
function is given below.- It increases the module approach to solve the problems.
- It enhances the re-usability of the program.
- We can do the coupling of the programs.
- It optimizes the code.
- It makes debugging easier.
- It makes development easy and creates less complexity.
Let's understand the basic concept of functions.
Defining a Function
A function can be defined by providing the name of the function with the appropriate parameter and return type. A function contains a set of statements which are called function body. The syntax is given below.
Syntax:
Let's understand the general syntax of the defining function.
- return_type - It can be any data type such as void, integer, float, etc. The return type must be matched with the returned value of the function.
- func_name - It should be an appropriate and valid identifier.
- parameter_list - It denotes the list of the parameters, which is necessary when we called a function.
- return value - A function returns a value after complete its execution.
Let's understand the following example.
Example - 1
Calling a Function
After creating a function, we can call or invoke the defined function inside the main() function
body. A function is invoked simply by its name with a parameter list, if any. The syntax is given below.Syntax:
Note - Calling function must be ended with semicolon (;).
When we call a function, the control is transferred to the called function. Then the called function executes all defined statements and returns the result to the calling function. The control returns to the main() function..
Example :
Passing Arguments to Function
When a function is called, it may have some information as per the function prototype is known as a parameter (argument). The number of parameters passed and data type while the function call must be matched with the number of parameters during function declaration. Otherwise, it will throw an error. Parameter passing is also optional, which means it is not compulsory to pass during function declaration. The parameter can be two types.
Actual Parameter - A parameter which is passed during a function definition is called the actual parameter.
Formal Parameter - A parameter which is passed during a function call is called the formal parameter.
We will learn more about the parameter in the next tutorial.
Return a Value from Function
A function always returns some value as a result to the point where it is called. The return keyword is used to return a value. The return statement is optional. A function can have only one return statement. The syntax is given below.
Syntax:
Example -
Function Examples
Let's understand the functions by using a program of adding two numbers using functions.
Dart Function with parameter and return value
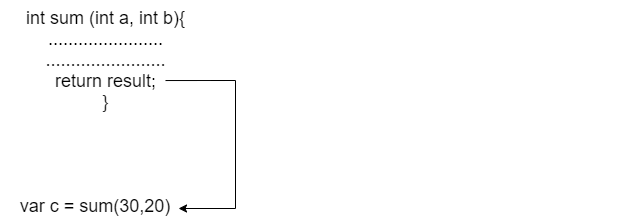
In the following example, we are creating a sum() function to add two number.
Example - 1
Output
Example of add two number using the function The sum of two numbers is: 50
Explanation:
In the above example, we declared a function named sum() and passed two integer variables as actual parameters. In the function body, we declared a result variable to store the sum of two numbers and returned the result.
In order to add two values, we called a function with the same name, passed formal parameters 30 and 20. The sum() returned a value which we stored in the variable c and printed the sum on the console.
Dart Function with No Parameter and Return Value
As we discussed earlier, the parameters are optional to pass while defining a function. We can create a function without parameter return value. The syntax is given below.
Syntax:
Let's understand the following example.
Example - 2
Output
Welcome to JavaTpoint
Explanation:
In the above example, we created a function named greetings() without argument and returned the string value to the calling function. Then, we called the greeting() function inside the print statement and printed the result to the console.
Dart Function with No Parameter and without a Return Value
We can declare a function without parameter and no return value. The syntax is given below.
Syntax:
In the above general syntax-
void - It represents the function has no return type.
fun_name - It represents the function name.
Let's understand the following example.
Example - 3
Output
The example of Dart Function Welcome to JavaTpoint
Explanation:
In the above example, we created a function called greeting() outside the main() function and writing the print statement. Inside the main() function, we called the defined function and printed the output to console.
Dart Function with Parameter and without a Return Value
We are creating a function to find the given number is even or odd. Let's understand the following example.
Example - 4
Output
The given number is even
Comments
Post a Comment