Dart Inheritance
Dart Inheritance
Dart inheritance is defined as the process of deriving the properties and characteristics of another class. It provides the ability to create a new class from an existing class. It is the most essential concept of the oops(Object-Oriented programming approach). We can reuse the all the behavior and characteristics of the previous class in the new class.
- Parent Class - A class which is inherited by the other class is called superclass or parent class. It is also known as a base class.
- Child Class - A class which inherits properties from other class is called the child class. It is also known as the derived class or subclass.
Suppose we have a fleet of cars, and we create three classes as Duster, Maruti, and Jaguar. The methods modelName(), milage(), and man_year() will be same for all of the three classes. By using the inheritance, we don't need to write these functions in each of the three classes.
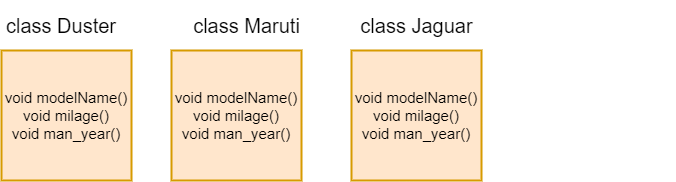
As you can see in the above figure, if we create class Car and write the common function in each of the classes. Then, it will increase duplication and data redundancy in the program. The inheritance is used to avoid this type of situation.
We can avoid data redundancy by defining the class Car with these functions in it and inheriting in the other classes from the Car class. It enhances the re-usability of code. We just need to write function one time instead of multiple times. Let's have a look at the following image.
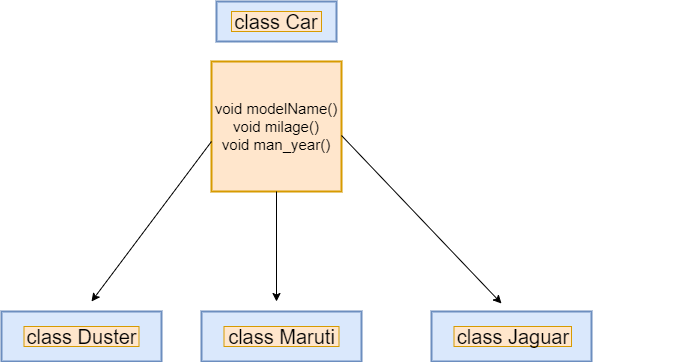
The syntax is given below.
Syntax -
The child class inherits functions and variables, or properties of parent class using the extends keyword. It cannot inherit the parent class constructor; we will discuss this concept later.
Types of Inheritance
The inheritance can be mainly four types. These are given below.
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
Single Level Inheritance
In the single inheritance, a class is inherited by a single class or subclass is inherited by one parent class. In the following example, we create Person which inherits Human class.
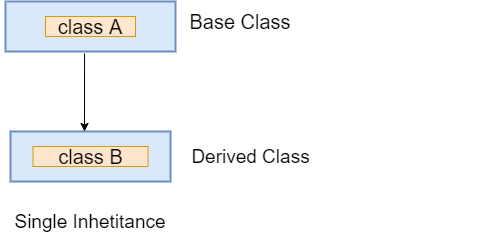
Let's understand the following example.
Example -
Output
The parrot can speak The bird can fly
Explanation:
In the above code, we create parent class Bird and declared the fly() function in it. Then, we created the child class called Parrot, which inherited the parent class's property using the extends keyword. The child class has its own function speak().
Now the child class has two functions fly() and speak(). So we created the object of child class and access both functions. It printed the result to the console.
Multilevel Inheritance
In the multiple inheritance, a subclass is inherited by another subclass or creates the chaining of inheritance. Let's understand the following example.
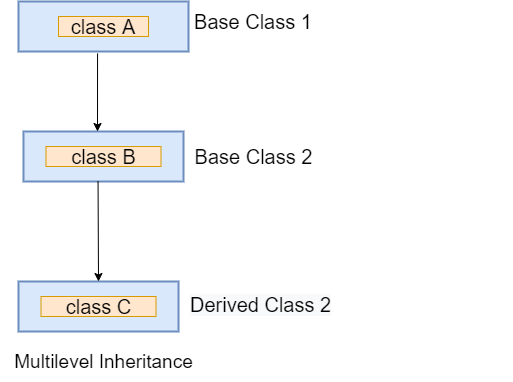
Example -
Output
The parrot can speak The bird can fly The eagle has a sharp vision
Explanation:
In the above example, we created another new class Eagle and inherited the Parrot class. Now the parrot is the parent class of Eagle, and class Eagle acquired all functions of both parent classes. We created the object of the child class and accessed all properties. It printed the output to the screen.
Note - Dart doesn't support multiple inheritance because it creates complexity in the program.
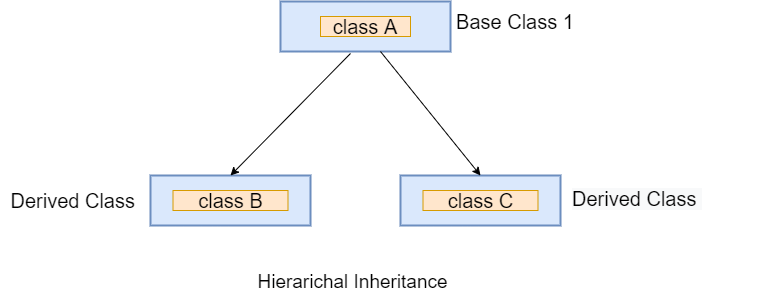
Hierarchical Inheritance
In the hierarchical inherence, two or more classes inherit a single class. In the following example, the two-child classes Peter and James inherit the Person class.
Example -
Output
James 24 Passed Peter 21 Computer Science
Comments
Post a Comment